FAILURE MODE AND EFFECT ANALYSIS
![]() Description
Description
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a method for structured identification of potential failures and analysis of risks.
![]() When
When
In the Analyse Causes phase.
![]() Goals
Goals
Identify key potential errors and risks. In the optimisation phase, you determine improvement actions for these potential errors.
![]() Steps
Steps
With the FMEA, we prioritise errors and risks based on the Risk Priority Number (RPN). Errors with a high RPN are key influencers on your process.
- Describe the process steps in the first column.
- For each process step, write down what could possibly go wrong.
- Describe what happens to the customer and process when the error occurs.
- Assess how severe this effect is (severity).
- Identify the causes of the error (use 5 x why to arrive at the root cause).
- Assess how often the error occurs (frequency of occurrence).
- Assess how long it takes for the error to be detected (likelihood of detection).
- Sort the 'Risk Priority Numbers' from high to low and discuss this with the team. Sorting helps to create focus within the team and start discussions about which process steps should be addressed first.
9. Establish concrete measures with responsible persons.
10. Implement the measures and reassess the 'frequency of occurrence' and 'likelihood of detection'. As a result of the measures taken, the potential failure will occur less frequently and/or be detected faster as soon as it occurs. The severity of the potential failure for the customer or process will remain the same in most cases.
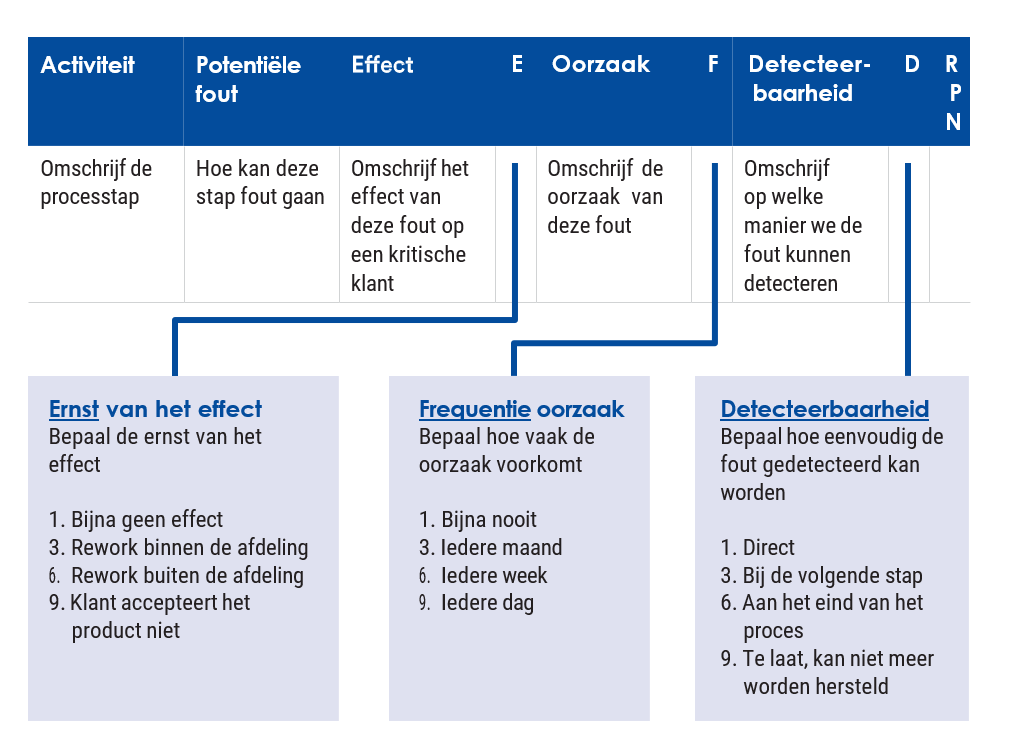
Figure: FMEA
![]() Examples
Examples
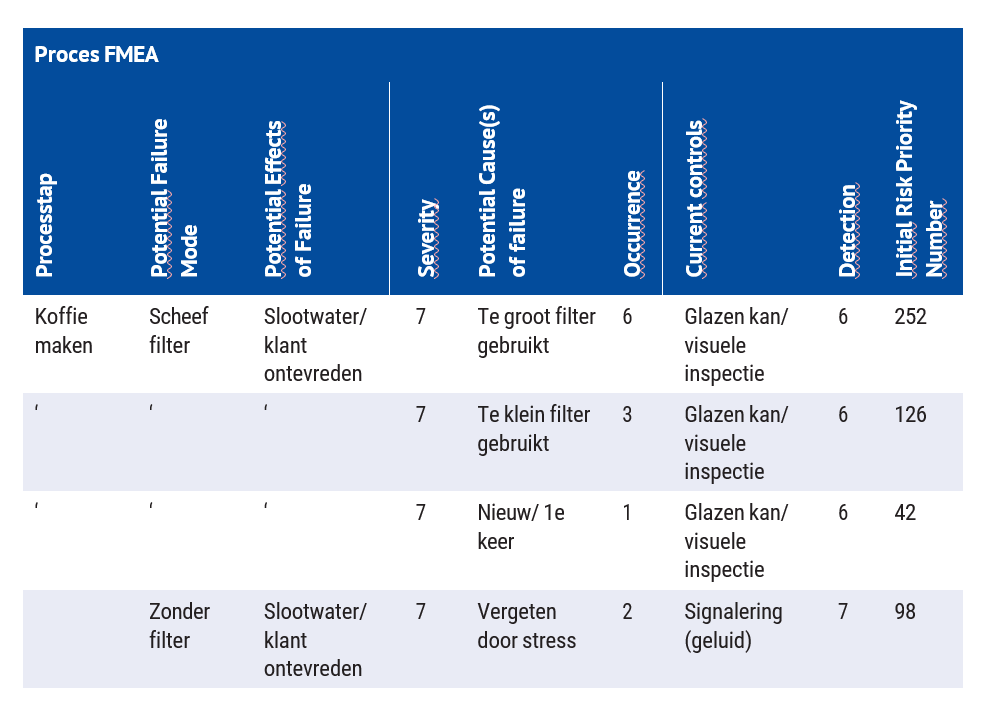
Here is an example of an FMEA:
![]() Tips:
Tips:
- Involve the (project) team in creating an FMEA.
- Pick up the disruption with the highest RPN.